How to Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally and Safely
February 13, 2026 | by syukr.adiwirya
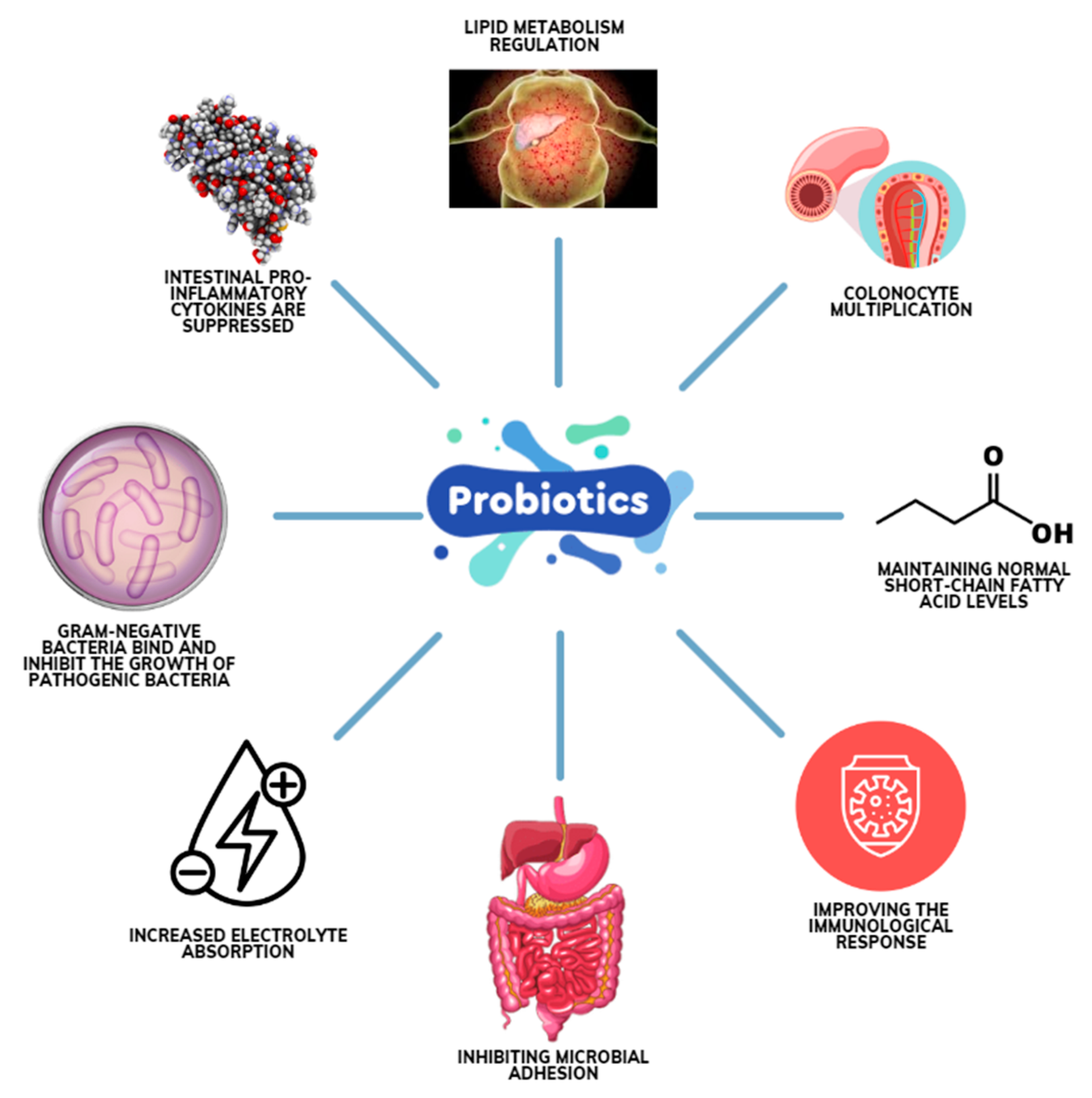
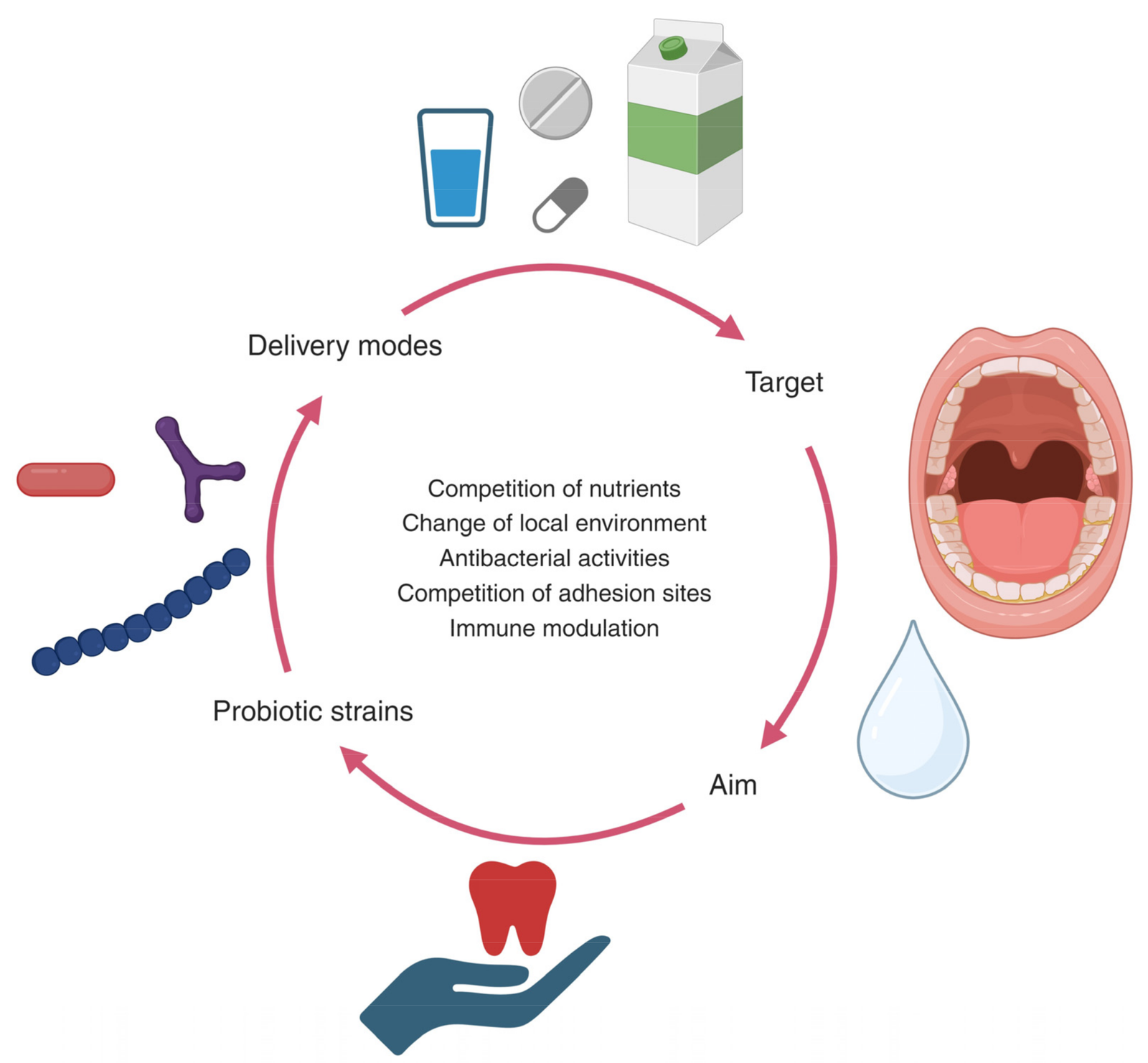
Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally: Gum disease starts with bacteria — specifically, harmful oral bacteria that accumulate in plaque along the gumline. When these microbes multiply unchecked, they trigger inflammation, bleeding, and eventually tissue damage. Many people search for ways to kill gum bacteria naturally, hoping to support their oral health using safer, plant-based, and evidence-aligned methods.
Dental science is clear: complete sterilization of the mouth is neither possible nor desirable. According to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (nidcr.nih.gov) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (cdc.gov), the goal is not to eliminate all bacteria but to control harmful strains and disrupt plaque biofilm. This article explains how to kill gum bacteria naturally using methods supported by dental education sources (.edu), public health organizations (.gov), and professional dental bodies (.org).
Natural methods work best when combined with consistent mechanical plaque removal and regular dental checkups.
Understanding Harmful Gum Bacteria
The human mouth contains hundreds of bacterial species. Many are beneficial or harmless. Problems arise when pathogenic bacteria dominate the gumline biofilm.
Dental microbiology programs at universities (.edu) identify several high-risk periodontal bacteria, including:
- Porphyromonas gingivalis
- Tannerella forsythia
- Treponema denticola
These bacteria:
- thrive in plaque layers
- produce inflammatory toxins
- break down gum tissue
- contribute to pocket formation
Natural antibacterial strategies aim to reduce their numbers and activity — not sterilize the mouth.
How to Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally — The Foundation Step
Before any natural antibacterial agent works, plaque must be physically disrupted.
According to ada.org, daily plaque removal is the most important factor in gum disease prevention.
Core mechanical steps:
- brush at gumline twice daily
- floss or use interdental cleaners
- clean tongue surface
- replace brush regularly
- brush at least two minutes
Without this step, natural antibacterials cannot penetrate biofilm effectively.
Salt Water Rinse Antibacterial Support
Salt water rinsing is widely recommended by dental schools (.edu) after oral procedures because it helps create an unfavorable environment for harmful bacteria.
Benefits:
- reduces bacterial load
- lowers swelling
- supports healing
- inexpensive and safe
Method:
- ½ teaspoon salt
- warm water
- rinse 30–45 seconds
- repeat 2–3 times daily
Salt does not sterilize — it supports bacterial control.
Essential Oils That Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally
Multiple laboratory and clinical studies indexed at ncbi.nlm.nih.gov show that certain essential oils have antimicrobial effects against oral pathogens.
Most studied oils:
- clove (eugenol)
- thyme (thymol)
- tea tree
- peppermint
- eucalyptus
Mechanisms include:
- bacterial membrane disruption
- enzyme interference
- biofilm inhibition
Professional essential-oil mouthrinses recognized by ada.org are built on this research foundation.
Always dilute before oral use.
Oil Pulling and Bacterial Reduction
Oil pulling is a traditional practice studied in several small controlled trials listed in government research databases (.gov indexed via PubMed).
Reported outcomes include:
- reduced plaque index
- reduced gingival index
- lower bacterial counts
Method:
- 1 tablespoon coconut or sesame oil
- swish gently 5–10 minutes
- spit out
- rinse
- brush
Oil pulling likely works through mechanical and lipid interaction effects rather than detoxification.
Oil-Based Gum Concentrate Application
An alternative to rinse methods is oil-based gum concentrate application, where botanical oils are applied directly along the gumline.
Supporters suggest this method may:
- increase contact time
- resist saliva dilution
- deliver antimicrobial botanicals locally
Educational product information at dentalpro7.com describes oil-based gum concentrate approaches designed for targeted gumline support rather than quick rinse exposure. These are described as adjunct gum-care tools.

How to Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally With Xylitol
Xylitol is a natural sugar alcohol widely studied in dental research (.edu and .gov publications).
Research findings show xylitol may:
- reduce harmful bacterial adhesion
- lower acid production
- interfere with bacterial metabolism
Common delivery:
- xylitol gum
- xylitol mints
- xylitol toothpaste
Use after meals for best support.
Green Tea Polyphenols and Oral Bacteria
University nutrition and dental departments (.edu) have studied green tea polyphenols for antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Observed actions:
- bacterial growth suppression
- antioxidant protection
- inflammation pathway moderation
Use as:
- unsweetened beverage
- cooled rinse
Avoid adding sugar.
Herbal Antibacterial Rinses
Herbal medicine references (.org) and integrative dental education programs (.edu) document antimicrobial activity in several herbs.
Most cited herbs:
- sage
- myrrh
- chamomile
- calendula
Simple herbal rinse:
- brew strong tea
- cool fully
- rinse
- discard
- make fresh daily
Alcohol-heavy tinctures may irritate gums.
Baking Soda Biofilm Control
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is referenced in dental education materials (.edu hygiene programs) as a mild antibacterial and acid-neutralizing agent.
Benefits:
- raises oral pH
- reduces acid-loving bacteria
- gentle abrasive
- odor reduction
Use occasionally — not as sole toothpaste.
Diet Strategies That Reduce Harmful Oral Bacteria
Public health nutrition sources (.gov dietary guidance) show diet influences oral bacterial balance.
Reduce:
- added sugars
- sticky carbs
- frequent snacking
Increase:
- fibrous vegetables
- lean proteins
- omega-3 fats
- vitamin C foods
Lower sugar frequency reduces bacterial fuel supply.
Hydration and Saliva Defense
Saliva is a natural antibacterial system emphasized in dental education (.edu).
Saliva helps:
- wash microbes
- neutralize acids
- supply protective proteins
- maintain pH balance
Support saliva by:
- drinking water often
- chewing xylitol gum
- avoiding tobacco
- limiting alcohol rinses
Dry mouth increases bacterial risk.
What Natural Methods Cannot Do
According to cdc.gov and nidcr.nih.gov, natural antibacterial methods cannot:
- remove tartar
- treat advanced periodontitis
- eliminate deep pocket infection
- reverse bone loss
- replace professional cleaning
They are preventive and supportive — not curative.
Warning Signs of Bacterial Gum Infection
See a dentist if you notice:
- bleeding beyond two weeks
- gum swelling
- persistent bad breath
- loose teeth
- gum recession
- pain when chewing
- pus discharge
Early treatment prevents progression.
How to Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally — Daily Protocol
Most effective natural bacterial control plan:
Morning:
- gumline brushing
- interdental cleaning
- essential oil rinse
Midday:
- xylitol gum
- water rinse
Evening:
- brush
- floss/interdental
- herbal or salt rinse
- oil-based gum concentrate (optional)
Weekly:
- oil pulling session
Consistency beats intensity.
✅ FAQ – How to Kill Gum Bacteria Naturally at Home
Q: Can I kill gum bacteria naturally without chemicals?
A: You can reduce harmful bacteria using brushing, flossing, essential oils, and xylitol support methods.
Q: Do natural antibacterials replace dental cleaning?
A: No. Professional cleanings remove tartar and deep plaque that home methods cannot.
Q: How fast does natural bacterial control work?
A: Early gum inflammation may improve within two to four weeks of consistent daily care.
 Gum Health Support Option — Dental Pro 7
Gum Health Support Option — Dental Pro 7
If you are building a daily natural gum care routine, some people prefer adding an oil-based gum concentrate for longer contact time along the gumline — instead of quick rinse exposure.
Dental Pro 7 is a botanical gum concentrate designed to support gumline care using oil-based delivery and plant-derived compounds.





Many natural oral care routines include brushing, interdental cleaning, and optional gum concentrate support.
 Checkout Dental Pro 7 Here
Checkout Dental Pro 7 Here
Other Articles: Best Essential Oils Gums
RELATED POSTS
View all